
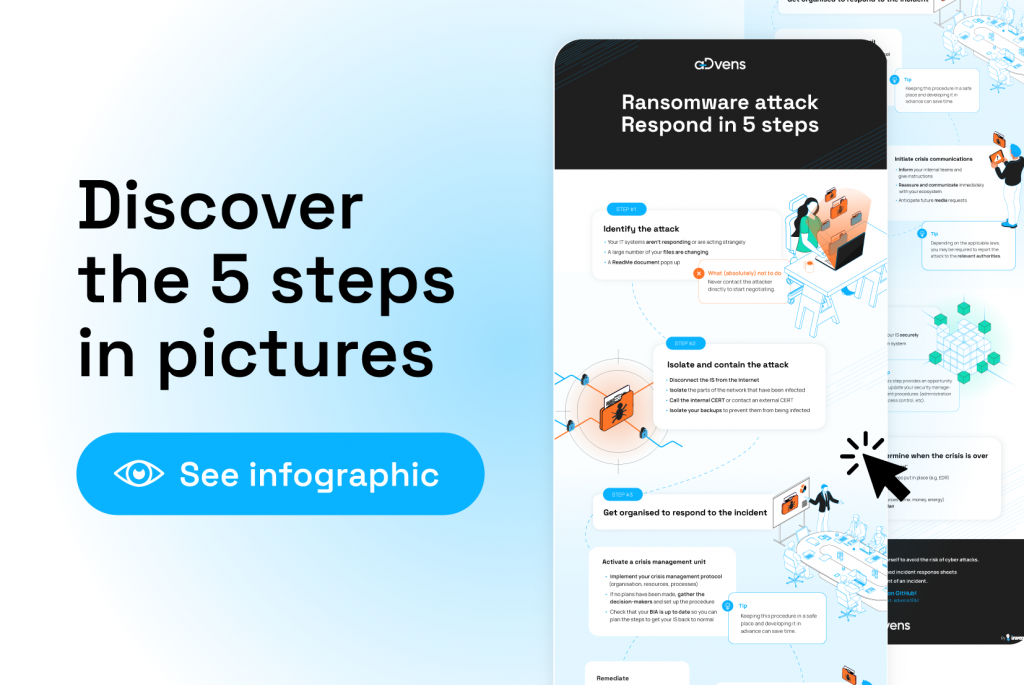
Ransomware attack, step 1: identify the signs early
Identifying the signs of an attack is the first key step in protecting yourself from ransomware and knowing how to respond. The three most common signs are:
- IT systems stop responding or act strangely.
- A large number of files change, indicating that a malicious program is encrypting the files.
- A document called something like ReadMe.txt appears, asking for a ransom in exchange for the key to decrypt the infected files. Do not reply to it!
Don’t panic, stay calm and follow these steps to respond effectively.
Ransomware: response and remediation steps
Step 2 – Isolate and contain the attack
To contain the ransomware attack, disconnect the IT and then isolate the infected parts of the network. Next, call your internal CERT or contact an external CERT. Remember to isolate your backups to prevent them from being infected.
Step 3 – Get organised to respond to the incident
To manage the incident in a structured way, you must take three measures simultaneously:
- Activate a crisis unit.
- Prepare crisis communications, both internally and externally.
- Establish and implement remediation measures.
Step 4 – Recover and rebuild your IT
Start by rebuilding the most compromised IT as securely as possible, before strengthening the other parts of the architecture.
Step 5 – Finalise and determine when the crisis is over
The attack is over! This is the time to make the return to normal “official” and maintain the tools and measures put in place (such as an EDR). You should then arrange an internal post-mortem to ensure you have the resources (time, money, energy) to finalise the security and protection plan against ransomware.
See the Advens CERT’s response to a ransomware attack:
When responding to a ransomware attack, reaction time is of the essence. And paying the ransom is never a good idea, as there is no guarantee that you’ll get your data back if you give in to blackmail. To help you stay informed about threats, the Advens CERT publishes joint incident response sheets with the SG CERT (formerly Société Générale), which are available on GitHub.


